Immune System Dysregulation
The immune system is one of the most complex and inclusive systems within the body. It should then be of no surprise, that if someone is suffering from any sort of ongoing issue such as pain, fatigue, digestive distress and so on, the immune system will be involved. More and more in my practice I am discovering and developing treatment approaches for overactive or underactive immune systems, the worst of these being auto-immune disease, where the body attacks its own tissue. Because of the increased prevalence of these conditions and the likelihood that you or someone close to you is experiencing an immune system irregularity, I have decided to write this somewhat technical newsletter. It is longer than most, but please make the time to read and digest the content. I promise you won’t regret it.
The immune system is a conglomeration of various cells and tissues designed to prevent foreign substances and organisms from causing damage to the body as a whole. It also works aggressively to promote healing and tissue repair after injury and to eliminate dead cells and improperly developing cells (cancer). The bulk of the immune system, located within the linings of the small and large intestine, is called the Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT). There is also another web of immune tissues in the linings of the nose, mouth, throat and lungs called the Bronchus Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT). Besides these areas, the organs most responsible for immune system support and function are the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and liver.
You are probably familiar with the term leukocytes, meaning white blood cells. These are the cells that increase in number when the body is trying to fight a recent (acute) infection. AIDS for example, is a condition in which certain white blood cells are in effect non-existent, making it virtually impossible for the AIDS patient to resist infection. There are several types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. For purposes of our discussion, I want to focus on the last type, the lymphocyte, and its role in fighting antigens and haptens. Antigens and haptens are any substances that, when present, generate an immune system response. Examples of antigens include bacteria, viruses and foreign proteins. Haptens are inorganic and consist of heavy metals, pesticides, chemicals etc.
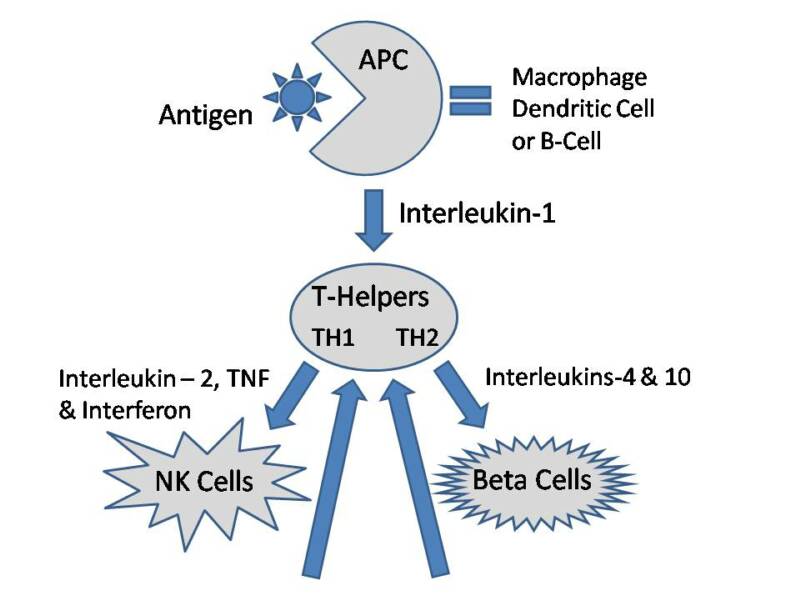
Take a look at the chart below. Here is basically what happens when an antigen or hapten appears in the body. First, it must be “tagged” or, if you will, marked for destruction and elimination. This is the job of the antigen-present cells (APC). Next, the APC sends out a specific chemical that acts as messengers, calling other important “helper” cells to the scene so that they can eliminate the antigen. The chemical messengers used by the immune system cells are called cytokines. They are listed by name next to the arrows on the chart. The first cytokine released comes from the APC and is called interleukin-1 (IL-1). Once IL-1 is detected, the helper cells can go to work. You can see that there are two arrows pointing away from the “T-Helpers” cell. One is directed toward NK cells and the other is directed toward Beta cells. In the early stages of antigen destruction, the immune system relies mostly on Natural Killer (NK) cells. If the infection is strong or lasts a long time, then more prominence is placed on the production of Beta cells. Beta cells are the ones that make antibodies to a substance. For instance, if you had the chicken pox as a child, you most likely have chicken pox antibodies in your blood, which ensures that you will no longer get that particular condition. After the cytokines have attracted the necessary cells, and the antigen has been eliminated, they must be turned off so that they do not continue to signal for help. This is the job of the Regulatory T-Cells and the Suppressor T-Cells. If all goes well, the cytokines are no longer produced, the antigen is eliminated and the body is now free from invasion/infection. Unfortunately, all too often, things do not go well.
The immune system is a conglomeration of various cells and tissues designed to prevent foreign substances and organisms from causing damage to the body as a whole. It also works aggressively to promote healing and tissue repair after injury and to eliminate dead cells and improperly developing cells (cancer). The bulk of the immune system, located within the linings of the small and large intestine, is called the Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT). There is also another web of immune tissues in the linings of the nose, mouth, throat and lungs called the Bronchus Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT). Besides these areas, the organs most responsible for immune system support and function are the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and liver.
You are probably familiar with the term leukocytes, meaning white blood cells. These are the cells that increase in number when the body is trying to fight a recent (acute) infection. AIDS for example, is a condition in which certain white blood cells are in effect non-existent, making it virtually impossible for the AIDS patient to resist infection. There are several types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. For purposes of our discussion, I want to focus on the last type, the lymphocyte, and its role in fighting antigens and haptens. Antigens and haptens are any substances that, when present, generate an immune system response. Examples of antigens include bacteria, viruses and foreign proteins. Haptens are inorganic and consist of heavy metals, pesticides, chemicals etc.
Take a look at the chart below. Here is basically what happens when an antigen or hapten appears in the body. First, it must be “tagged” or, if you will, marked for destruction and elimination. This is the job of the antigen-present cells (APC). Next, the APC sends out a specific chemical that acts as messengers, calling other important “helper” cells to the scene so that they can eliminate the antigen. The chemical messengers used by the immune system cells are called cytokines. They are listed by name next to the arrows on the chart. The first cytokine released comes from the APC and is called interleukin-1 (IL-1). Once IL-1 is detected, the helper cells can go to work. You can see that there are two arrows pointing away from the “T-Helpers” cell. One is directed toward NK cells and the other is directed toward Beta cells. In the early stages of antigen destruction, the immune system relies mostly on Natural Killer (NK) cells. If the infection is strong or lasts a long time, then more prominence is placed on the production of Beta cells. Beta cells are the ones that make antibodies to a substance. For instance, if you had the chicken pox as a child, you most likely have chicken pox antibodies in your blood, which ensures that you will no longer get that particular condition. After the cytokines have attracted the necessary cells, and the antigen has been eliminated, they must be turned off so that they do not continue to signal for help. This is the job of the Regulatory T-Cells and the Suppressor T-Cells. If all goes well, the cytokines are no longer produced, the antigen is eliminated and the body is now free from invasion/infection. Unfortunately, all too often, things do not go well.
The immune system is one of the most complex and inclusive systems within the body. It should then be of no surprise, that if someone is suffering from any sort of ongoing issue such as pain, fatigue, digestive distress and so on, the immune system will be involved. More and more in my practice I am discovering and developing treatment approaches for overactive or underactive immune systems, the worst of these being auto-immune disease, where the body attacks its own tissue. Because of the increased prevalence of these conditions and the likelihood that you or someone close to you is experiencing an immune system irregularity, I have decided to write this somewhat technical newsletter. It is longer than most, but please make the time to read and digest the content. I promise you won’t regret it.
The immune system is a conglomeration of various cells and tissues designed to prevent foreign substances and organisms from causing damage to the body as a whole. It also works aggressively to promote healing and tissue repair after injury and to eliminate dead cells and improperly developing cells (cancer). The bulk of the immune system, located within the linings of the small and large intestine, is called the Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT). There is also another web of immune tissues in the linings of the nose, mouth, throat and lungs called the Bronchus Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT). Besides these areas, the organs most responsible for immune system support and function are the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and liver.
You are probably familiar with the term leukocytes, meaning white blood cells. These are the cells that increase in number when the body is trying to fight a recent (acute) infection. AIDS for example, is a condition in which certain white blood cells are in effect non-existent, making it virtually impossible for the AIDS patient to resist infection. There are several types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. For purposes of our discussion, I want to focus on the last type, the lymphocyte, and its role in fighting antigens and haptens. Antigens and haptens are any substances that, when present, generate an immune system response. Examples of antigens include bacteria, viruses and foreign proteins. Haptens are inorganic and consist of heavy metals, pesticides, chemicals etc.
Take a look at the chart below. Here is basically what happens when an antigen or hapten appears in the body. First, it must be “tagged” or, if you will, marked for destruction and elimination. This is the job of the antigen-present cells (APC). Next, the APC sends out a specific chemical that acts as messengers, calling other important “helper” cells to the scene so that they can eliminate the antigen. The chemical messengers used by the immune system cells are called cytokines. They are listed by name next to the arrows on the chart. The first cytokine released comes from the APC and is called interleukin-1 (IL-1). Once IL-1 is detected, the helper cells can go to work. You can see that there are two arrows pointing away from the “T-Helpers” cell. One is directed toward NK cells and the other is directed toward Beta cells. In the early stages of antigen destruction, the immune system relies mostly on Natural Killer (NK) cells. If the infection is strong or lasts a long time, then more prominence is placed on the production of Beta cells. Beta cells are the ones that make antibodies to a substance. For instance, if you had the chicken pox as a child, you most likely have chicken pox antibodies in your blood, which ensures that you will no longer get that particular condition. After the cytokines have attracted the necessary cells, and the antigen has been eliminated, they must be turned off so that they do not continue to signal for help. This is the job of the Regulatory T-Cells and the Suppressor T-Cells. If all goes well, the cytokines are no longer produced, the antigen is eliminated and the body is now free from invasion/infection. Unfortunately, all too often, things do not go well.
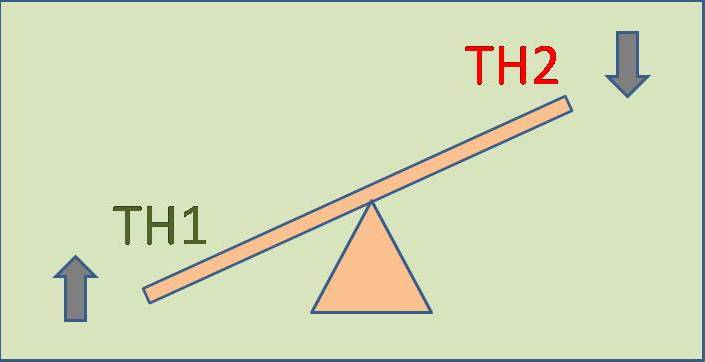
It is common for the bodies of “normal” or “healthy” people to be internally adapting to a dysregulated immune system on a daily basis, and to have been doing so for decades. Constant adaptation comes at a great expense. Eventually the reserves and tissues responsible for continuing the adaptation process, fatigue and finally fail. It is the case of a leaky roof. If left alone significant future damage is certain. The most common dysregulation is an imbalance between the two types of helper cells. They are categorized as TH1 and TH2 (see chart). Often there is too much immune system action with one of these categories. In long standing illness, the TH2 side is often still running at a very high level while the TH1 side is essentially suppressed. Most asthma patients for example, have a great deal of TH2 activity. The way to calm this down is twofold. First, we want to directly slow down the side that is too active. Next, we want to increase the side that is underactive. Before we decrease the overactive side, we must make sure that there is not a reason the immune system is working. In other words, is an antigen still present? Is the body currently trying to get rid of something, or has it somehow become stuck in park with the engine revved? Most of the patients I see have had a long standing problem, so it is therefore unlikely that they are still actively fighting an infection. Instead, their bodies have lost the ability to regulate and get back into balance - a very common phenomenon.
The immune system is a conglomeration of various cells and tissues designed to prevent foreign substances and organisms from causing damage to the body as a whole. It also works aggressively to promote healing and tissue repair after injury and to eliminate dead cells and improperly developing cells (cancer). The bulk of the immune system, located within the linings of the small and large intestine, is called the Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT). There is also another web of immune tissues in the linings of the nose, mouth, throat and lungs called the Bronchus Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT). Besides these areas, the organs most responsible for immune system support and function are the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and liver.
You are probably familiar with the term leukocytes, meaning white blood cells. These are the cells that increase in number when the body is trying to fight a recent (acute) infection. AIDS for example, is a condition in which certain white blood cells are in effect non-existent, making it virtually impossible for the AIDS patient to resist infection. There are several types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. For purposes of our discussion, I want to focus on the last type, the lymphocyte, and its role in fighting antigens and haptens. Antigens and haptens are any substances that, when present, generate an immune system response. Examples of antigens include bacteria, viruses and foreign proteins. Haptens are inorganic and consist of heavy metals, pesticides, chemicals etc.
Take a look at the chart below. Here is basically what happens when an antigen or hapten appears in the body. First, it must be “tagged” or, if you will, marked for destruction and elimination. This is the job of the antigen-present cells (APC). Next, the APC sends out a specific chemical that acts as messengers, calling other important “helper” cells to the scene so that they can eliminate the antigen. The chemical messengers used by the immune system cells are called cytokines. They are listed by name next to the arrows on the chart. The first cytokine released comes from the APC and is called interleukin-1 (IL-1). Once IL-1 is detected, the helper cells can go to work. You can see that there are two arrows pointing away from the “T-Helpers” cell. One is directed toward NK cells and the other is directed toward Beta cells. In the early stages of antigen destruction, the immune system relies mostly on Natural Killer (NK) cells. If the infection is strong or lasts a long time, then more prominence is placed on the production of Beta cells. Beta cells are the ones that make antibodies to a substance. For instance, if you had the chicken pox as a child, you most likely have chicken pox antibodies in your blood, which ensures that you will no longer get that particular condition. After the cytokines have attracted the necessary cells, and the antigen has been eliminated, they must be turned off so that they do not continue to signal for help. This is the job of the Regulatory T-Cells and the Suppressor T-Cells. If all goes well, the cytokines are no longer produced, the antigen is eliminated and the body is now free from invasion/infection. Unfortunately, all too often, things do not go well.
It is common for the bodies of “normal” or “healthy” people to be internally adapting to a dysregulated immune system on a daily basis, and to have been doing so for decades. Constant adaptation comes at a great expense. Eventually the reserves and tissues responsible for continuing the adaptation process, fatigue and finally fail. It is the case of a leaky roof. If left alone significant future damage is certain. The most common dysregulation is an imbalance between the two types of helper cells. They are categorized as TH1 and TH2 (see chart). Often there is too much immune system action with one of these categories. In long standing illness, the TH2 side is often still running at a very high level while the TH1 side is essentially suppressed. Most asthma patients for example, have a great deal of TH2 activity. The way to calm this down is twofold. First, we want to directly slow down the side that is too active. Next, we want to increase the side that is underactive. Before we decrease the overactive side, we must make sure that there is not a reason the immune system is working. In other words, is an antigen still present? Is the body currently trying to get rid of something, or has it somehow become stuck in park with the engine revved? Most of the patients I see have had a long standing problem, so it is therefore unlikely that they are still actively fighting an infection. Instead, their bodies have lost the ability to regulate and get back into balance - a very common phenomenon.
Here are some of the practical steps to help immune system regulation:
1.) Increase TH1 Function when low – add substances like echinacea, zinc, astragulus, and goldenseal
2.) Increase TH2 function when low – add substances like green tea, caffeine, white willow and grape seed extract
3.) Decrease TH1 or TH2 function – done by getting rid of the cytokines that continue to signal for
help. This is done in the liver through detoxification. Glycine, a prevalent amino acid, is often used
4.) Increase overall immune regulation (modulators) – Vitamin D, EPA, DHA, glutathione
5.) Neuro-Immune balance – this is an important hands-on step where specific stimulation of immune
reflexes is performed along with other “desensitization” techniques, to override a habitual neurologic pathway.
When a dysregulated immune system is present, just about any symptom could result. Recognized conditions from long term adaptation however, include all the autoimmune diseases, multiple chemical sensitivities (MCS), Chronic Fatigue, Fibromyalgia, Hypothyroidism, and so many more. For instance, in a sample of 1582 respondents in 2004 from the Atlanta, Georgia, it was found that 12.6% reported multiple chemical hypersensitivity. The prevalence for MCS is similar to that (15.9%) found by the California Department of Health Services for their state in 1999 and suggests that the national prevalence may be similar. This number is more than double what it was just ten years ago. In fact, just about all chronic conditions are on the rise and even more so in children.
The number of American children with chronic illnesses has quadrupled since the time when some of their parents were children. Just pause and think what that will mean for future healthcare costs. According to a study done at Harvard and published in a special edition of the Journal of the American Medical Association on Children’s health, an almost fourfold increase in childhood obesity in the past three decades, twice the asthma rates since the 1980s, and a jump in the number of attention deficit disorder cases are driving the growth of chronic illnesses among children. In 1960, just 1.8 percent of American children and adolescents were reported to have a chronic health condition that limited their activities. In 2004, the rate rose to 7 percent.
Because these numbers are steadily going up, it seems logical that immune compromised and nutritionally deficient people are now giving birth to, and raising immune compromised and nutritionally deficient children. It also needs to be mentioned that the dietary habits of most children (a direct result of poor parenting) are abominable, further perpetuating a worsening state.
Autoimmune Disease
Continuous signaling by the cytokines is one of the methods of auto-immune disease. Another method is the process by which a native or harmless substance becomes tagged for destruction, when in fact it should be left alone. There are a number of autoimmune diseases that you are familiar with. Autoimmune disease of the joint is called Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA); autoimmune disease of the sheath around nerves is called Multiple Sclerosis (MS); autoimmune disease of the pancreas is called Type I Diabetes Mellitus; autoimmune disease of the small intestine is called, Crohn's disease. Autoimmune diseases are a major threat to the health of all Americans. At least ten million Americans suffer from the more than eighty illnesses caused by autoimmunity. They are a special threat to women (75%), whose prevalence is three times that of men (25%). Autoimmune diseases are among the ten leading causes of death among women in all age groups up to 65.
I treat patients with these diseases on a regular basis. However, one of the most common autoimmune diseases that many have, but that is often wrongly diagnosed, is one that relates to the thyroid gland. In the United States, the most common cause of hypothyroidism after the age of six years old is auto-immune thyroid disease (Hashimoto’s) . Hashimoto’s has strong connection to females with estrogen dominance or polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) , those with Celiac Disease and even those with dental amalgams (mercury fillings) . In the case of PCOS, a study reported in the European Journal of Endocrinology, 2004, showed that 42.3% of women with PCOS had evidence of autoimmune thyroid disease as detected by ultrasound. Despite the fact that Hashimoto’s is the primary cause of hypothyroidism and the blood test is inexpensive, almost no one diagnosed with hypothyroidism is screened to see if they have antibodies against their own thyroid tissue, which is clear-cut diagnostic evidence of Hashimoto’s. The reason for this I suppose is a combination of ignorance and apathy. Why?
Even if Hashimoto’s is detected, there is little that can be done by traditional medicine. Their treatment of choice is Synthroid or some other thyroid medication. These do nothing to prevent the disease, they just supply the hormone that can no longer be made properly because the thyroid is being destroyed. This approach, in my opinion, is greatly insufficient. The body is not just a bunch of parts as most traditional medical doctors to often believe. The thyroid gland is an important component of the endocrine system - the complex organization of tissues that make and regulate hormones. When the thyroid fails, great stress is placed upon the pituitary gland, the adrenal glands, the pancreas, the ovaries and even the liver. Chances are, that one of the reasons the thyroid failed in the first place was because of a combination of prolonged stresses on these related tissues some time in the recent or distant past. I have written at length about these ubiquitous functional problems in previous newsletters. Had they been addressed on a preventative basis perhaps a great deal of present misery could have been avoided.
1.) Increase TH1 Function when low – add substances like echinacea, zinc, astragulus, and goldenseal
2.) Increase TH2 function when low – add substances like green tea, caffeine, white willow and grape seed extract
3.) Decrease TH1 or TH2 function – done by getting rid of the cytokines that continue to signal for
help. This is done in the liver through detoxification. Glycine, a prevalent amino acid, is often used
4.) Increase overall immune regulation (modulators) – Vitamin D, EPA, DHA, glutathione
5.) Neuro-Immune balance – this is an important hands-on step where specific stimulation of immune
reflexes is performed along with other “desensitization” techniques, to override a habitual neurologic pathway.
When a dysregulated immune system is present, just about any symptom could result. Recognized conditions from long term adaptation however, include all the autoimmune diseases, multiple chemical sensitivities (MCS), Chronic Fatigue, Fibromyalgia, Hypothyroidism, and so many more. For instance, in a sample of 1582 respondents in 2004 from the Atlanta, Georgia, it was found that 12.6% reported multiple chemical hypersensitivity. The prevalence for MCS is similar to that (15.9%) found by the California Department of Health Services for their state in 1999 and suggests that the national prevalence may be similar. This number is more than double what it was just ten years ago. In fact, just about all chronic conditions are on the rise and even more so in children.
The number of American children with chronic illnesses has quadrupled since the time when some of their parents were children. Just pause and think what that will mean for future healthcare costs. According to a study done at Harvard and published in a special edition of the Journal of the American Medical Association on Children’s health, an almost fourfold increase in childhood obesity in the past three decades, twice the asthma rates since the 1980s, and a jump in the number of attention deficit disorder cases are driving the growth of chronic illnesses among children. In 1960, just 1.8 percent of American children and adolescents were reported to have a chronic health condition that limited their activities. In 2004, the rate rose to 7 percent.
Because these numbers are steadily going up, it seems logical that immune compromised and nutritionally deficient people are now giving birth to, and raising immune compromised and nutritionally deficient children. It also needs to be mentioned that the dietary habits of most children (a direct result of poor parenting) are abominable, further perpetuating a worsening state.
Autoimmune Disease
Continuous signaling by the cytokines is one of the methods of auto-immune disease. Another method is the process by which a native or harmless substance becomes tagged for destruction, when in fact it should be left alone. There are a number of autoimmune diseases that you are familiar with. Autoimmune disease of the joint is called Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA); autoimmune disease of the sheath around nerves is called Multiple Sclerosis (MS); autoimmune disease of the pancreas is called Type I Diabetes Mellitus; autoimmune disease of the small intestine is called, Crohn's disease. Autoimmune diseases are a major threat to the health of all Americans. At least ten million Americans suffer from the more than eighty illnesses caused by autoimmunity. They are a special threat to women (75%), whose prevalence is three times that of men (25%). Autoimmune diseases are among the ten leading causes of death among women in all age groups up to 65.
I treat patients with these diseases on a regular basis. However, one of the most common autoimmune diseases that many have, but that is often wrongly diagnosed, is one that relates to the thyroid gland. In the United States, the most common cause of hypothyroidism after the age of six years old is auto-immune thyroid disease (Hashimoto’s) . Hashimoto’s has strong connection to females with estrogen dominance or polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) , those with Celiac Disease and even those with dental amalgams (mercury fillings) . In the case of PCOS, a study reported in the European Journal of Endocrinology, 2004, showed that 42.3% of women with PCOS had evidence of autoimmune thyroid disease as detected by ultrasound. Despite the fact that Hashimoto’s is the primary cause of hypothyroidism and the blood test is inexpensive, almost no one diagnosed with hypothyroidism is screened to see if they have antibodies against their own thyroid tissue, which is clear-cut diagnostic evidence of Hashimoto’s. The reason for this I suppose is a combination of ignorance and apathy. Why?
Even if Hashimoto’s is detected, there is little that can be done by traditional medicine. Their treatment of choice is Synthroid or some other thyroid medication. These do nothing to prevent the disease, they just supply the hormone that can no longer be made properly because the thyroid is being destroyed. This approach, in my opinion, is greatly insufficient. The body is not just a bunch of parts as most traditional medical doctors to often believe. The thyroid gland is an important component of the endocrine system - the complex organization of tissues that make and regulate hormones. When the thyroid fails, great stress is placed upon the pituitary gland, the adrenal glands, the pancreas, the ovaries and even the liver. Chances are, that one of the reasons the thyroid failed in the first place was because of a combination of prolonged stresses on these related tissues some time in the recent or distant past. I have written at length about these ubiquitous functional problems in previous newsletters. Had they been addressed on a preventative basis perhaps a great deal of present misery could have been avoided.
Where Does It Come From?
Autoimmune diseases of all sorts have no precise cause. Researchers around the world search for environmental, genetic, hormonal and nutritional clues, without much success. In my personal experience, I have seen Hashimoto’s associated most commonly with mineral imbalances, heavy metal toxicity and viral infections. However, as I preach on a regular basis, and write about in my article, Anything Can Cause Anything, all of the systems in the body are connected. Therefore, almost any conceivable internal or external cause is possible. In the case of Hashimoto’s, the most common associations I have found with applied kinesiology are: excess copper in the thyroid, a positive viral test within the thyroid only, and the thyroid hormone T3 strengthening a patient while at the same time, weakening the patient when placed over the thyroid. This last sign is almost definitive - when a substance needed for optimal health, actually weakens a patient over its related organ, immune dysregulation is to be expected. Beyond these signs there is likely to be present a host of other issues related to different systems. Insulin resistance, adrenal gland fatigue, neurotransmitter imbalances, mineral imbalances and foreign microorganisms are common.
The immune system dysregulation patterns I have described above are an ever increasing phenomenon related to any number of structural, chemical and/or emotional stresses. Despite their complexity, these imbalances can be addressed through natural and alternative means and often with amazing results.
Autoimmune diseases of all sorts have no precise cause. Researchers around the world search for environmental, genetic, hormonal and nutritional clues, without much success. In my personal experience, I have seen Hashimoto’s associated most commonly with mineral imbalances, heavy metal toxicity and viral infections. However, as I preach on a regular basis, and write about in my article, Anything Can Cause Anything, all of the systems in the body are connected. Therefore, almost any conceivable internal or external cause is possible. In the case of Hashimoto’s, the most common associations I have found with applied kinesiology are: excess copper in the thyroid, a positive viral test within the thyroid only, and the thyroid hormone T3 strengthening a patient while at the same time, weakening the patient when placed over the thyroid. This last sign is almost definitive - when a substance needed for optimal health, actually weakens a patient over its related organ, immune dysregulation is to be expected. Beyond these signs there is likely to be present a host of other issues related to different systems. Insulin resistance, adrenal gland fatigue, neurotransmitter imbalances, mineral imbalances and foreign microorganisms are common.
The immune system dysregulation patterns I have described above are an ever increasing phenomenon related to any number of structural, chemical and/or emotional stresses. Despite their complexity, these imbalances can be addressed through natural and alternative means and often with amazing results.